subdermal rfid chip A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. This type of subdermal implant usually contains a . See more Nintendo 3DS NFC Reader / Writer for Amiibo complete New in Box NIB. Brand New. C .ACR122U NFC RFID 13.56MHz Contactless Smart Reader Writer W/ 5 mifare 1k cards. .
0 · rfid microchip implant
1 · rfid microchip
2 · rfid chip technology
3 · rfid chip implantation
4 · rfid chip for subway
5 · rfid chip for credit card
6 · rfid chip australia
7 · microchip vs rfid
Proceed as follows: First open the Settings app on your iPhone. Then select the option “Control .
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. This type of subdermal implant usually contains a . See more
• 1998: The first experiments with a radio-frequency identification (RFID) implant were carried out in 1998 by the British scientist Kevin Warwick. . See more
rfid microchip implant
rfid microchip
• Brain implant• Skin• Dental implant See moreFor Microchip implants that are encapsulated in silicate glass, there exists multiple methods to embed the device subcutaneously ranging from placing the microchip implant in a syringe or trocar and piercing under the flesh (subdermal) then releasing the . See moreInfectionInfection has been cited as a source of failure within RFID and related microchip implanted individuals, either due to improper implantation techniques, implant rejections or corrosion of implant elements. See moreDespite a lack of evidence demonstrating invasive use or even technical capability of microchip implants, they have been the subject of many conspiracy theories.The Southern Poverty Law Center reported in 2010 that on the Christian right, there were concerns that . See more
A few jurisdictions have researched or preemptively passed laws regarding human implantation of microchips.United StatesIn the United States, many states such as Wisconsin (as . See moreThe general public are most familiar with microchips in the context of identifying pets.In popular cultureImplanted individuals are considered to be grouped together as part of the transhumanism See more Are you ready for an RFID implant? Here’s everything what you should know about RFID chips before you implant them into your body.A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
Are you ready for an RFID implant? Here’s everything what you should know about RFID chips before you implant them into your body. The tiny, grain-of-rice-size RFID (radio frequency identification) chip opens doors with a wave of your hand in front of a chip reader. And at Pause Fest, an Australian tech expo, 10 VIPs. RFID microchips, embedded under the skin with a procedure that’s already cheap and available, provide a digital interface to the real world centered about the holder’s identity: your ID, credit card information, bus pass, library card, and many other sources of information you currently carry in your purse/wallet can instead be stored on an .
Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards. Chips sold for implants are generally either low or high frequency. RFID chips are identified using radio waves, and near-field communication (NFC) chips are a branch of high-frequency. Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical terms,.
It's a useful technology application: insert a subdermal radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip somewhere the animal can't get to it – such as the nape of its neck – and a whole world of digital data opens up. Today, more than 50,000 people have elected to have a subdermal chip surgically inserted between the thumb and index finger, serve as their new swipe key, or credit card. RFID microchips can be used as passwords or keys, while NFC chips can be used to store electronic credit cards or cryptocurrencies. The implants themselves are shaped like cylinders, which contain a biologically safe epoxy resin, the microchip, and a copper antenna coil.A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
rfid chip technology
Are you ready for an RFID implant? Here’s everything what you should know about RFID chips before you implant them into your body. The tiny, grain-of-rice-size RFID (radio frequency identification) chip opens doors with a wave of your hand in front of a chip reader. And at Pause Fest, an Australian tech expo, 10 VIPs. RFID microchips, embedded under the skin with a procedure that’s already cheap and available, provide a digital interface to the real world centered about the holder’s identity: your ID, credit card information, bus pass, library card, and many other sources of information you currently carry in your purse/wallet can instead be stored on an . Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards.
Chips sold for implants are generally either low or high frequency. RFID chips are identified using radio waves, and near-field communication (NFC) chips are a branch of high-frequency. Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical terms,.
It's a useful technology application: insert a subdermal radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip somewhere the animal can't get to it – such as the nape of its neck – and a whole world of digital data opens up.
Today, more than 50,000 people have elected to have a subdermal chip surgically inserted between the thumb and index finger, serve as their new swipe key, or credit card.
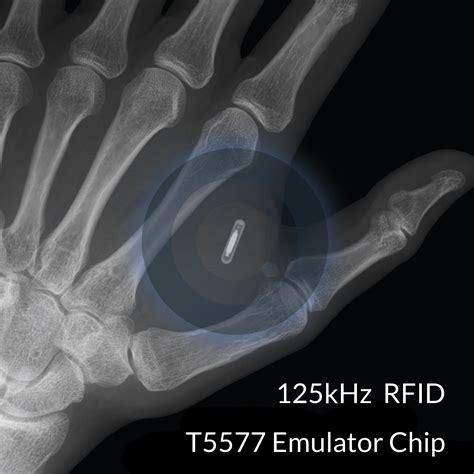

rfid chip implantation

rfid chip for subway
rfid chip for credit card
rfid chip australia
Inverid's ReadID personal app, ReadID Me (previously known as NFC Passport Reader) reads and verifies the NFC chip embedded in electronic passports and other.
subdermal rfid chip|rfid chip implantation