all about rfid chips RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person. Developer's Description. NFC mobile payment app. NFC mobile payment app. Save you card track data and pay in shops with contactless card readers using your mobile phone. Add the cards using a mini .
0 · where are rfid chips used
1 · what makes something rfid
2 · what does rfid look like
3 · types of rfid chips
4 · rfid is involved when using
5 · rfid for personal use
6 · how does rfid scanning work
7 · how do rfid chips work
How to Design an NFC Business Card with Adobe Photoshop. Read on to find out .
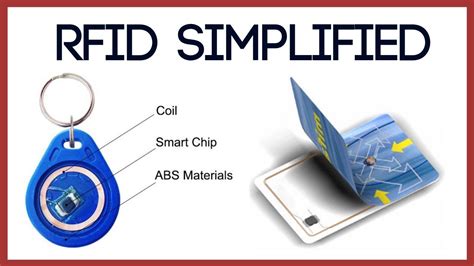
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.A radio-frequency identification system uses tags, or labels attached to the objects to be identified. Two-way radio transmitter-receivers called interrogators or readers send a signal to the tag and read its response. RFID tags are made out of three pieces: • a micro chip (an integrated circuit which stores and processes information and An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio .
nfc south standings 2015
This diagram shows the role of an RFID chip in a transponder. Image Credit: RFID Handbook Types of RFID Chips. The Engineering360 SpecSearch database categorizes RFID chips according to the type of device (passive, active, or semi-passive) in which the chips are used. Passive devices are RFID tags without batteries. They draw power from the . Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a type of passive wireless technology that allows for tracking or matching of an item or individual. The system has two basic parts: tags and readers. RFID chips come in different storage capacities, which can range from just enough to store a unique identifier (a few bits) to larger capacities capable of storing large amounts of data about a tagged item (a few kilobytes). The choice of memory size depends on the needs of the application, ranging from simple identification (such as product . Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object or person. It uses radio frequency to search, identify, track, and communicate with items and people. RFID (Radio Frequency .
All About Cards offers a wide product portfolio with RFID chips from well-known manufacturers such as MIFARE® from NXP Semiconductors or LEGIC. To avoid time-consuming reading processes when inserting a card, the RFID cards can be perfectly used for access control, time tracking or cashless payment applications.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) cards are used for tracking, identification, and access control. The cards integrate an RFID microchip that holds all the data needed for specific applications. The RFID cards use different frequency bands, including 125 kHz Low Frequency (LF), 13.56 MHz High Frequency (HF), and 860-960 Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). Stores more data: RFID chips store their information in the form of Electronic Product Code (EPC) and user memory. EPC memory is used to store a specific EPC number that is associated solely with that chip and typically contains 96-128 bits, while some have more. In order for this EPC number to tell us anything about the item, it needs to be . The process begins when the RFID chip is powered by the electromagnetic field generated by the reader. When a credit card with an RFID chip is held near an RFID reader, the reader emits a specific frequency of radio waves. These waves activate the RFID chip, enabling it to send a unique identification code or other relevant data to the reader.
FD chipless RFID finds better use in IoT applications. Chipless RFID Sensors The traditional RFID tags offer sensing applications via the use of sensors along with chips. The sensor whether it is a temperature sensor, humidity, toxic gas sensor, or fill-level sensor, is embedded with the chip. In the case of chipless RFID tags, there is no IC.LEGIC Identsystems AG is a leading supplier of contactless RFID chip cards. In addition to MIFARE® cards, they are among the most widely used smart cards in RFID technology. All chips operate on the 13.56 MHz frequency and comply with the ISO standards ISO 15693, ISO/IEC 14443, ISO 18092 (NFC) and the prime RF standard.The technology can be used to label people and products, however RFID chips can carry more information, making them useful for identifying assets like prescription pharmaceuticals, blood, livestock and high-ticket items. Because RFID tags can be customized and programmed, encrypted and password-protected, they are suited to secure applications . RFID tags are rugged and robust and can work in harsh temperatures and environment. The RFID system works at a remarkably high speed, even in adverse conditions. RFID tags are available in different shapes, sizes, types and materials. The information on the read-only tag cannot be altered or duplicated. Read-write tags can be used repeatedly.
RFID chips are integrated circuits inside RFID tags containing all the components of a controller, memory, and microprocessor. They carry and transmit objects’ information. RFID chips are categorized by frequency — Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), Ultra High Frequency (UHF), and Microwave Frequency.
RFID chip (Photo Credit : Maschinenjunge /Wikimedia Commons) RFID: An Improvement On Barcodes. In the supermarket, you’re likely to come across a barcode (or QR code) on the products stacked in the racks. These bar . When you cross the border, the border agent can scan the passport, and the machine can read the data from the RFID chip. RFID chips are also used in credit cards with contactless payments. When you tap a credit card to pay for something, the machine reads an RFID chip embedded in the card. They're also used for transit systems, tolls, and . Additionally, be aware that some RFID chips operate at different frequency ranges, and not all blocking materials may be suitable for all types of RFID chips. Understand the specific frequencies at which the RFID chip .
Passive RFID chips rely on the energy transmitted by the reader, which can restrict their range and functionality. Active RFID chips with their own power source can overcome this limitation, but their larger size hinders miniaturization efforts. 2. Antenna design: The size reduction of RFID chips also affects the design and performance of the .
The RFID chip in the label stores data, which can be a simple identifier or more complex information depending on the type of chip and its memory capacity. This data is encoded in a specific format that the reader can interpret. When the label is within range of a compatible reader, the chip is powered, and it transmits the stored data to the .RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology is becoming increasingly popular around the world, and RFID chip stickers, as the core of this technology, play an important role in various industries. Whether it is inventory management in the retail industry or equipment tracking in the medical field, RFID chip stickers provide great convenience for data collection and automated .
Discover the leading manufacturers of RFID chips and explore their innovative technology in this insightful article. Find out who makes RFID chips and stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in this field. The ease of hacking also depends on the chip itself. RFID chips are all made differently, some better at securing data than others. In fact, many RFID cards run on different frequencies, which hackers can’t target all at once. Considering all of these factors, it’s very unlikely that your RFID chip will be hacked, especially since companies . RFID chips, the most important part of RFID tags, play a crucial role. RFID chip usually has a built-in antenna and an integrated circuit IC. Antennas can send and receive radio waves, while IC is responsible for modulating and demodulating radio signals, as well as processing and storing data. According.Like all RFID labels, dual technology RFID labels contain a chip that sits inside an inlay alongside an antenna, which helps send and receive the information stored on the chip. Dual technology inlays can come in various formats, like discrete pocket tags embedded in your garment or hang tags that are easy for customers to see and access.
Many argue that RFID chips are the obvious choice to replace aging barcodes and QR codes that never really caught on -- and in a perfect world, they would. Barcodes only hold 10 to 12 characters of information while a single RFID chip can hold 2 KB of data. Not only that, they can be written and re-written as many times as necessary.Working with the RFID industry to better understand, where RFID can be found, what power levels and frequencies are being used in different locations, and how to best mitigate potential EMI with .First of all: Readers/scanners for RFID chips transmit normal radio waves, like radio or television, just at shorter wavelengths. The chips respond to the magnetic field of the readers with such weak signals that even the readers have difficulties in perceiv-ing them. Thus even at a distance of just a few meters the radio emissions are noChip cards as contact and contactless chip cards/RFID cards: We print chip cards for you according to your wishes and have the suitable card printer for printing yourself. . For coding your cards with contact or contactless chips, All About Cards offers a variety of professional devices. For all common chips, such as Mifare, Infineon, Atmel .
nfc west standings by year
where are rfid chips used
nfc north standings today
what makes something rfid
what does rfid look like
The original key has a 7 bytes UID and the second Key has a 4 byte UID. This is the first problem. You cannot store a 7 byte UID into a 4 byte field. You'd need to get a different NFC card/tag. The second key is not UID changeable. Usually the biggest problem, as most systems rely on the UID stored in sector 0, which you cannot overwrite.
all about rfid chips|where are rfid chips used