nfc reader frequency NFC is rooted in radio-frequency identification technology (known as RFID) which allows compatible hardware to both supply power to and communicate with an otherwise . See more
Many SIM cards provided by wireless carriers also contain a secure element. Android 4.4 and higher provide an additional method of card emulation that doesn't involve a secure element, called host-based card emulation. This .
0 · what is nfc rfid
1 · rfid or nfc card
2 · rfid frequency chart
This game was one of redemption for the 49ers, who had been eliminated from the playoffs by the Packers in each of the three previous seasons. This game-winn.

NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s. See moreNear-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (1+1⁄2 in) or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through . See moreAlthough the range of NFC is limited to a few centimeters, standard plain NFC is not protected against eavesdropping and can be vulnerable to data modifications. Applications may use higher-layer cryptographic protocols to establish a secure channel. See moreNFC allows one- and two-way communication between endpoints, suitable for many applications.NFC devices can act . See more
NFC standards cover communications protocols and data exchange formats and are based on existing radio-frequency identification (RFID) standards including ISO/IEC 14443 See more
NFC is rooted in radio-frequency identification technology (known as RFID) which allows compatible hardware to both supply power to and communicate with an otherwise . See moreNFC is a set of short-range wireless technologies, typically requiring a separation of 10 cm (3+7⁄8 in) or less. NFC operates at 13.56 See more
NFC standards cover communications protocols and data exchange formats, and are based on existing RFID standards including See more Near-field communication devices operate at the same frequency (13.56 MHz) .NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s. Near-field communication devices operate at the same frequency (13.56 MHz) as HF RFID readers and tags. The standards and protocols of the NFC format is based on RFID standards outlined in ISO/IEC 14443, FeliCa, and the basis for parts of ISO/IEC 18092.
what is nfc rfid
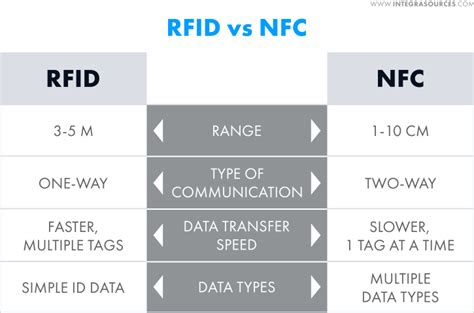
NFC is a newer, high-frequency version of RFID, and also involves both tags and readers. NFC's higher frequency means that, while it can transfer data much faster than RFID, it only works from a distance of about 4 cm/1.6 in or less. Meanwhile, RFID works from a distance of up to 12 m/40 ft. Determining whether a card is RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) or NFC (Near Field Communication) enabled can be quite straightforward with some simple methods. Here are three methods to help you identify if a card contains RFID or NFC technology: NFC devices operate at the same frequency as high frequency RFID readers and tags — 13.56 MHz. But unlike RFID devices and tags, NFC does not have a range from 25 meters to 100 meters. Instead, NFC takes advantage of the short read range limitations of .
Reader/writer – enables devices to read data stored on tags embedded in access cards or key fobs. Peer-to-peer – enables NFC devices to communicate with each other to exchange data. In this mode, an NFC device can act as both a reader and a tag.NFC is a special form of high-frequency RFID technology, and its operating frequency is usually maintained in the 13.56 MHz band. In addition, the reading distance of NFC technology is relatively short, generally within 10 centimeters. Common NFC devices include readers, smart cards, and mobile payments. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency systems can range 25 feet or more. RFID can also help a company keep costs down, improve data capture or meet other requirements. This technology operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz and follows the ISO/IEC 18092 standard. NFC readers are equipped with an antenna that allows them to establish a connection with other NFC-enabled devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and .
How far can NFC read? NFC has a typical read range of only a few centimeters, around 4 cm or 1.5 in on average. 3. What is the difference between HF RFID and NFC? NFC is a subset of the HF frequency range for RFID. HF RFID tags operate anywhere between 3 and 30 MHz on the Electromagnetic Spectrum, while NFC tags only operate on 13.56 MHz.
NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s.
Near-field communication devices operate at the same frequency (13.56 MHz) as HF RFID readers and tags. The standards and protocols of the NFC format is based on RFID standards outlined in ISO/IEC 14443, FeliCa, and the basis for parts of ISO/IEC 18092. NFC is a newer, high-frequency version of RFID, and also involves both tags and readers. NFC's higher frequency means that, while it can transfer data much faster than RFID, it only works from a distance of about 4 cm/1.6 in or less. Meanwhile, RFID works from a distance of up to 12 m/40 ft.
smart id cards
Determining whether a card is RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) or NFC (Near Field Communication) enabled can be quite straightforward with some simple methods. Here are three methods to help you identify if a card contains RFID or NFC technology: NFC devices operate at the same frequency as high frequency RFID readers and tags — 13.56 MHz. But unlike RFID devices and tags, NFC does not have a range from 25 meters to 100 meters. Instead, NFC takes advantage of the short read range limitations of . Reader/writer – enables devices to read data stored on tags embedded in access cards or key fobs. Peer-to-peer – enables NFC devices to communicate with each other to exchange data. In this mode, an NFC device can act as both a reader and a tag.
smart gas card
NFC is a special form of high-frequency RFID technology, and its operating frequency is usually maintained in the 13.56 MHz band. In addition, the reading distance of NFC technology is relatively short, generally within 10 centimeters. Common NFC devices include readers, smart cards, and mobile payments. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency systems can range 25 feet or more. RFID can also help a company keep costs down, improve data capture or meet other requirements. This technology operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz and follows the ISO/IEC 18092 standard. NFC readers are equipped with an antenna that allows them to establish a connection with other NFC-enabled devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and .
rfid or nfc card
rfid frequency chart
Step 6: Tap on Payment default. Step 7: Select the app you use most often and want to pay with every time you tap your phone at a terminal. Step 8: Now, tap on Use default. Step 9: Choose .
nfc reader frequency|rfid frequency chart