chip rfid 2014 • 1998: The first experiments with a radio-frequency identification (RFID) implant were carried out in 1998 by the British scientist Kevin Warwick. His implant was used to open doors, switch on lights, and cause verbal output within a building. After nine days the implant was removed and has since been held in the Science Museum in London. The Flipper just emulates a NFC reader, but not a POS device which actually pulls more data. Yes you get the card number, but that NOT the only data that gets pulled over if you interface .
0 · where are rfid chips used
1 · types of rfid chips
2 · rfid chips in humans
3 · rfid chips for sale
4 · rfid chip pros and cons
5 · rfid chip meaning
6 · rfid chip manufacturing
7 · pros and cons of rfid
NFC wird nicht unterstützt; Um die Karte weiterhin kostenlos zu nutzen, muss man monatlich das offene Saldo vom Girokonto überweisen. Dafür hat man jeweils 10 Tage nach Rechnungsstellung Zeit. . Die Santander 1plus Visa .
Scientists at the Wyoming Institute of Technology (WIT) have determined that a shocking 1 in 3 Americans has been implanted with an RFID microchip. In an article published .• 1998: The first experiments with a radio-frequency identification (RFID) implant were carried out in 1998 by the British scientist Kevin Warwick. His implant was used to open doors, switch on lights, and cause verbal output within a building. After nine days the implant was removed and has since been held in the Science Museum in London. Scientists at the Wyoming Institute of Technology (WIT) have determined that a shocking 1 in 3 Americans has been implanted with an RFID microchip. In an article published this week, they detail.Microchip implant (human) A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a fast developing technology that utilizes radio waves for data collection and transfer (Rosenbaum, 2014). Historically, RFID technology has been used in supply chain management, primarily to track goods in warehouses (Bowen, Wingrave, Klanchar, and Craighead, 2013).In 2014, the world RFID market was worth US.89 billion, up from US.77 billion in 2013 and US.96 billion in 2012. This figure includes tags, readers, and software/services for RFID cards, labels, fobs, and all other form factors. . The 134 kHz RFID chips, from VeriChip Corp. can incorporate personal medical information and could save .Health Care Based Human RFID Implants. RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et . RFID. R adio-frequency identification (RFID) technology has been in use for over 50 years. The technology involves a microchip attached to an antenna, which responds to an incoming signal from a reader by sending an outgoing signal.
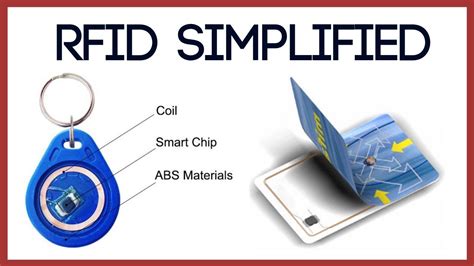
1. Introduction to RFIDs. Concepts of ambient intelligence and pervasive computing include the integration of small chips and. sensors in everyday items to make them "smart". Smart things can.The RFID reader is a network-connected device that can be portable or permanently attached. It uses radio waves to transmit signals that activate the tag. Once activated, the tag sends a wave back to the antenna, where it is translated into data. The transponder is in the RFID tag itself. The opponents of human-implanted RFID chips argue that such chips are associated with security risks, cause health problems, contradict to religious doctrines, and may be forcefully implemented in employees. Abstract: Radio frequency identification (RFID) sensors have received increasing attention in recent years due to their wireless battery-free operation, low profile, simplicity, low cost, and multimodality sensitivity.
Scientists at the Wyoming Institute of Technology (WIT) have determined that a shocking 1 in 3 Americans has been implanted with an RFID microchip. In an article published this week, they detail.Microchip implant (human) A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a fast developing technology that utilizes radio waves for data collection and transfer (Rosenbaum, 2014). Historically, RFID technology has been used in supply chain management, primarily to track goods in warehouses (Bowen, Wingrave, Klanchar, and Craighead, 2013).In 2014, the world RFID market was worth US.89 billion, up from US.77 billion in 2013 and US.96 billion in 2012. This figure includes tags, readers, and software/services for RFID cards, labels, fobs, and all other form factors. . The 134 kHz RFID chips, from VeriChip Corp. can incorporate personal medical information and could save .Health Care Based Human RFID Implants. RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et . RFID. R adio-frequency identification (RFID) technology has been in use for over 50 years. The technology involves a microchip attached to an antenna, which responds to an incoming signal from a reader by sending an outgoing signal.
1. Introduction to RFIDs. Concepts of ambient intelligence and pervasive computing include the integration of small chips and. sensors in everyday items to make them "smart". Smart things can.The RFID reader is a network-connected device that can be portable or permanently attached. It uses radio waves to transmit signals that activate the tag. Once activated, the tag sends a wave back to the antenna, where it is translated into data. The transponder is in the RFID tag itself. The opponents of human-implanted RFID chips argue that such chips are associated with security risks, cause health problems, contradict to religious doctrines, and may be forcefully implemented in employees.
nfc tag versions wiki
where are rfid chips used
types of rfid chips
rfid chips in humans

Can be password protected with NFC Tools: Yes Remark: Cheap with a good .
chip rfid 2014|rfid chip manufacturing