rfid tag classes Comparing RFID tag types: UHF vs. HF vs. NFC vs. LF RFID. There are a variety of RFID tags on the market today, differentiated by frequency range (low, high and ultra-high). Each RFID type can be either active (powered), passive . There are some NFC system apps that may need permissions to run. Q5 screwed with permissions for me so much I just reset with a clean reformat and no issues. 2. transurfer • 4 .
0 · rfid tag writing software
1 · rfid tag reader and writer
2 · rfid tag programmer kit
3 · rfid tag number format
4 · programmable rfid stickers
5 · how to program rfid reader
6 · how to program rfid cards
7 · how to configure rfid card
Now we can start interacting with NFC/RFID tags using the following functions: .
RFID tag range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can effectively read the tag’s information. This range is influenced by several factors, including the type of tag, the power of the reader, and environmental conditions. Comparing RFID tag types: UHF vs. HF vs. NFC vs. LF RFID. There are a variety of RFID tags on the market today, differentiated by frequency range (low, high and ultra-high). Each RFID type can be either active .RFID tag range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can effectively read the tag’s information. This range is influenced by several factors, including the type of tag, the power of the reader, and environmental conditions. Comparing RFID tag types: UHF vs. HF vs. NFC vs. LF RFID. There are a variety of RFID tags on the market today, differentiated by frequency range (low, high and ultra-high). Each RFID type can be either active (powered), passive .
Here is a breakdown of the classes as originally proposed. • Class 1: a simple, passive, read-only backscatter tag with one-time, field-programmable non-volatile memory. • Class 2: a passive backscatter tag with up to 65 kilobytes of read-write memory.Antenna, microchip and battery are the essential elements of these RFID tags. They are further classified into three types; active, passive and semi-passive. In today’s blog, we discuss RFID tag types and compare them based on frequency, performance, speed and usage. Before moving ahead, users must know the functions of basic elements of RFID .
RFID tag types can be classified as low-frequency, high-frequency, and ultra-high-frequency. RFID cards typically use one of these three frequencies to communicate via radio waves. Almost every RFID type we can see can be active (powered), passive (un-powered), or semi-passive (battery-assisted).Radio Waves. The electromagnetic spectrum is composed of various frequencies of waves that are produced using electromagnetic energy. A radio wave is essentially a disturbance through space that carries energy from one place to another. Radio waves oscillate, in that, while traveling the energy continuously rises and falls in intensity. Class 2 tags would be read-write and feature user memory. Class 3 tags would be semi-passive tags, suitable for use with sensors. Class 4 tags would be active tags. And class 5 tags would be RFID tags with onboard computing power that could form mesh networks and communicate with each other.Want to know the difference between the different types of RFID tags? We talk about passive, semi-passive and active RFID tags and their characteristics.
RFID tags can be divided into five classes as shown in the following table: RFID reader - The readers usually are mainly active type and will read information either transmitted by RFID tags or reflected by them. RFID reader usually is interfaced with computer. What is RFID? RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification.RFID tags are classified as Class 0 through Class 5, depending on their functionality: (Class-1 Gen-2 RFID tags are backward-compatible with Gen-1 Class-0 and Class 1 tags.) The full Gen-2 EPCglobal specification is available here.RFID tag range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can effectively read the tag’s information. This range is influenced by several factors, including the type of tag, the power of the reader, and environmental conditions. Comparing RFID tag types: UHF vs. HF vs. NFC vs. LF RFID. There are a variety of RFID tags on the market today, differentiated by frequency range (low, high and ultra-high). Each RFID type can be either active (powered), passive .
Here is a breakdown of the classes as originally proposed. • Class 1: a simple, passive, read-only backscatter tag with one-time, field-programmable non-volatile memory. • Class 2: a passive backscatter tag with up to 65 kilobytes of read-write memory.
rfid tag writing software
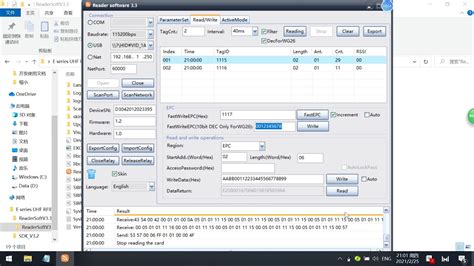
rfid tag reader and writer
Antenna, microchip and battery are the essential elements of these RFID tags. They are further classified into three types; active, passive and semi-passive. In today’s blog, we discuss RFID tag types and compare them based on frequency, performance, speed and usage. Before moving ahead, users must know the functions of basic elements of RFID . RFID tag types can be classified as low-frequency, high-frequency, and ultra-high-frequency. RFID cards typically use one of these three frequencies to communicate via radio waves. Almost every RFID type we can see can be active (powered), passive (un-powered), or semi-passive (battery-assisted).

Radio Waves. The electromagnetic spectrum is composed of various frequencies of waves that are produced using electromagnetic energy. A radio wave is essentially a disturbance through space that carries energy from one place to another. Radio waves oscillate, in that, while traveling the energy continuously rises and falls in intensity.
Class 2 tags would be read-write and feature user memory. Class 3 tags would be semi-passive tags, suitable for use with sensors. Class 4 tags would be active tags. And class 5 tags would be RFID tags with onboard computing power that could form mesh networks and communicate with each other.Want to know the difference between the different types of RFID tags? We talk about passive, semi-passive and active RFID tags and their characteristics.RFID tags can be divided into five classes as shown in the following table: RFID reader - The readers usually are mainly active type and will read information either transmitted by RFID tags or reflected by them. RFID reader usually is interfaced with computer. What is RFID? RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification.

rfid tag programmer kit
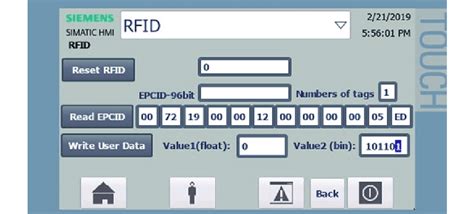
what is pvc smart card
On-Metal NXP NTAG®213 NFC Label 30x30mm quantity. Add to basket. SKU: .
rfid tag classes|how to program rfid reader