stanford rf id When a person holds an ID card up to an RFID receiver, an antenna in the ID card harvests a tiny bit of RFID energy from the receiver and uses this to generate a code that it then beams back to the receiver. The above steps have saved your original SIM card data on the computer. Now we .
0 · Stanford id card office
1 · Stanford id card magstripes
2 · Stanford id card appointment
SCORES; Day Date Opponent Score Location Venue Attendance; NFC Wild Card Playoff: Sun: 1/8/2017: H: New York Giants: 38-13: W: Green Bay, WI: Lambeau Field: 77549: NFC .
Now, Stanford engineers have developed a way to detect physiological signals emanating from the skin with sensors that stick like band-aids and beam wireless readings to a receiver clipped onto clothing. When a person holds an ID card up to an RFID receiver, an antenna in the ID card harvests a tiny bit of RFID energy from the receiver and uses this to generate a code that it then beams back to the receiver.
Now, Stanford engineers have developed a way to detect physiological signals emanating from the skin with sensors that stick like band-aids and beam wireless readings to a receiver clipped onto clothing. When a person holds an ID card up to an RFID receiver, an antenna in the ID card harvests a tiny bit of RFID energy from the receiver and uses this to generate a code that it then beams back to the receiver. Their eventual design met these parameters with a variation of the RFID – radiofrequency identification – technology used to control keyless entry to locked rooms.The Stanford ID Card Office oversees the production of new and replacement cards, maintains a card information database of students, faculty and staff; installs and maintains card readers; and assists in developing new Stanford ID Card applications.
Stanford researchers at the Bao Research Group have patented a body area sensor network (bodyNET) that can be used to monitor human physiological signals for next-generation personalized healthcare.Stanford University Catalog . Academic Calendar 2022-23 Schedule of Classes Bulletin Archive Get Help Academic Calendar 2022-23 . and embedded systems) and the communications capabilities (RFID, Bluetooth, wireless sensor networks, Wi-Fi, Low Power WANs, cellular networks, vehicular communications). Students will apply the acquired knowledge .Uses novel RFID/NFC technology. Receiver and transmitter can be close together. Can operate on multiple frequencies. Platform has many possible variations. Novel features: First intrinsic stretchable NFC wireless sensor tag on skin. First intrinsic NFC stretchable antenna. First intrinsic stretchable nF level capacitor.
STANFORD - The same technology that prevents thefts in clothing stores could also help surgeons keep track of instruments and gauze sponges during medical procedures, according to a preliminary study at the Stanford University School of Medicine. Stanford University researchers have now developed a tiny wireless chip that can go inside the cell to report evidence on some of those mysteries. A team led by electrical engineers Ada Poon and H.S. Philip Wong has created a chip system based on radio frequency identification device (RFID) technology, similar to the RFID tags found on .Presenting a realistic and professional view of RFID and contactless technology, this book is ideal for practising electronics and computer engineers working in auto ID, and on the design of RFID products and new security systems. Now, Stanford engineers have developed a way to detect physiological signals emanating from the skin with sensors that stick like band-aids and beam wireless readings to a receiver clipped onto clothing.
When a person holds an ID card up to an RFID receiver, an antenna in the ID card harvests a tiny bit of RFID energy from the receiver and uses this to generate a code that it then beams back to the receiver. Their eventual design met these parameters with a variation of the RFID – radiofrequency identification – technology used to control keyless entry to locked rooms.
The Stanford ID Card Office oversees the production of new and replacement cards, maintains a card information database of students, faculty and staff; installs and maintains card readers; and assists in developing new Stanford ID Card applications.Stanford researchers at the Bao Research Group have patented a body area sensor network (bodyNET) that can be used to monitor human physiological signals for next-generation personalized healthcare.Stanford University Catalog . Academic Calendar 2022-23 Schedule of Classes Bulletin Archive Get Help Academic Calendar 2022-23 . and embedded systems) and the communications capabilities (RFID, Bluetooth, wireless sensor networks, Wi-Fi, Low Power WANs, cellular networks, vehicular communications). Students will apply the acquired knowledge .Uses novel RFID/NFC technology. Receiver and transmitter can be close together. Can operate on multiple frequencies. Platform has many possible variations. Novel features: First intrinsic stretchable NFC wireless sensor tag on skin. First intrinsic NFC stretchable antenna. First intrinsic stretchable nF level capacitor.
STANFORD - The same technology that prevents thefts in clothing stores could also help surgeons keep track of instruments and gauze sponges during medical procedures, according to a preliminary study at the Stanford University School of Medicine. Stanford University researchers have now developed a tiny wireless chip that can go inside the cell to report evidence on some of those mysteries. A team led by electrical engineers Ada Poon and H.S. Philip Wong has created a chip system based on radio frequency identification device (RFID) technology, similar to the RFID tags found on .
no rf reading cb
Stanford id card office
mifare 1k card frequency
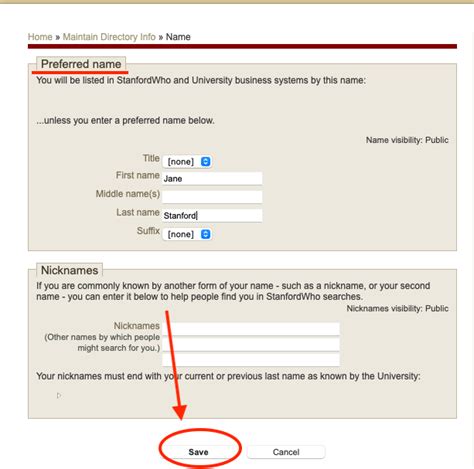
Stanford id card magstripes
rfid 行业从业者,现在越来越多的企业会使用rfid,诚然,rfid的标签和使用成本是远高于条码的。 1,电子标签本身的价格是远高于条码标签的。 2,手持设备,虽然现在基本上,手持RFID读取器都是采用安卓的,但成本上还是高于条码手持读取器的。
stanford rf id|Stanford id card office