rfid chips research Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, with a clock reading 90 seconds to midnight. The authoritative guide to ensuring science and technology make life on Earth better, not worse. An x-ray showing a Walletmor RFID chip injected into a person’s hand after a local anesthetic. Near Field Communication (NFC) is a fast, intuitive technology that lets you interact securely .Scanning a QR code on your iPhone is easy with our online QR Reader. Follow these simple steps: Access our QR Code reader tool on your iPhone. Click on the “Scan QR Code” option available right there. Point your camera at the QR .
0 · Smaller Chips Open Door to New RFID Applications
1 · A Review of RFID Sensors, the New Frontier of Internet of Things
I have this same problem with my iPhone 12. I can read and write to NTAG 215 .
Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to .
3. Chip Based RFID Sensors. There exist two implementations of a sensor employing a chip, . Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip’s design makes it possible to embed RFID tags into high value chips, such as computer chips, boosting supply chain security for high-end technologies.3. Chip Based RFID Sensors. There exist two implementations of a sensor employing a chip, namely the electronic RFID sensor and the electromagnetic one. A sketch representing the two topologies is shown in Figure 4. Both configurations contain the same functional units, but with a fundamental difference in the sensing part. Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, with a clock reading 90 seconds to midnight. The authoritative guide to ensuring science and technology make life on Earth better, not worse. An x-ray showing a Walletmor RFID chip injected into a person’s hand after a local anesthetic.
Researchers have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip's design makes it possible to.
Smaller Chips Open Door to New RFID Applications
A Review of RFID Sensors, the New Frontier of Internet of Things
Or, RFID tags can be placed in parking garages to measure occupancy and map where and how many spaces are being used. A chip could be added to the floor of every space; when a car pulls into the spot and covers the light-sensitive sensor, the tag recognizes that the spot is occupied and can send that information to a central location. Health Care Based Human RFID Implants. RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et al., 2022, p. 7). We demonstrate that a 25 \ (\upmu \) m wireless radio frequency identification (RFID) device can not only be taken up by a mammalian cell but can also be detected and specifically. Then, it has been demonstrated how RFID sensors in conjunction with artificial intelligence and machine learning can be applied for enhancing RFID tag sensitivity and selectivity to a high degree of accuracy.
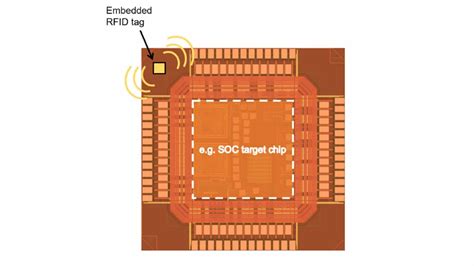
Researchers at MIT and Texas Instruments have developed a new type of radio frequency identification (RFID) chip that is virtually impossible to hack. The first part provides an overview of microchip development and applications, drawing attention to augmented bodies used for access control, payment, and tracking. The second part provides an overview of surveillance and the prevailing views of surveillance as a tool of power, discipline, and/or control. Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip’s design makes it possible to embed RFID tags into high value chips, such as computer chips, boosting supply chain security for high-end technologies.
3. Chip Based RFID Sensors. There exist two implementations of a sensor employing a chip, namely the electronic RFID sensor and the electromagnetic one. A sketch representing the two topologies is shown in Figure 4. Both configurations contain the same functional units, but with a fundamental difference in the sensing part. Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, with a clock reading 90 seconds to midnight. The authoritative guide to ensuring science and technology make life on Earth better, not worse. An x-ray showing a Walletmor RFID chip injected into a person’s hand after a local anesthetic.
Researchers have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip's design makes it possible to. Or, RFID tags can be placed in parking garages to measure occupancy and map where and how many spaces are being used. A chip could be added to the floor of every space; when a car pulls into the spot and covers the light-sensitive sensor, the tag recognizes that the spot is occupied and can send that information to a central location.
Health Care Based Human RFID Implants. RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et al., 2022, p. 7). We demonstrate that a 25 \ (\upmu \) m wireless radio frequency identification (RFID) device can not only be taken up by a mammalian cell but can also be detected and specifically. Then, it has been demonstrated how RFID sensors in conjunction with artificial intelligence and machine learning can be applied for enhancing RFID tag sensitivity and selectivity to a high degree of accuracy. Researchers at MIT and Texas Instruments have developed a new type of radio frequency identification (RFID) chip that is virtually impossible to hack.
afc and nfc wild card games

Compatibility: NFC Tools for Android, iOS, PC / Mac Can be password protected .
rfid chips research|Smaller Chips Open Door to New RFID Applications