difference between gen2 and gen 3 rfid tags The second-generation system (Gen-2) is favored after December 2004 and is the standard to follow when satisfying the requirements of the DoD and Wal-Mart RFID mandates. RFID tags are classified as Class 0 through Class 5, depending on their functionality: Class 0 – UHF; read . Click "Write" to be prompted with an NFC "Ready to Scan" message. Now your smartphone is looking for an NFC tag to encode. For iPhone, hold the top-center of your phone within 1 inch of Tap Tag while this message is up (as seen in .There are 3 requirements for making amiibos you can use on your Switch/Wii U/3DS. NFC writing capability - generally this means only Android phones with NFC, but apparently it is possible to buy an NFC reader/writer for PC but it is .
0 · rfid tags for access control
1 · rfid tags and readers
2 · new rfid tags not working
3 · low frequency rfid tags
4 · how to program rfid tags
5 · facility code rfid tags
6 · access rfid tags and readers
Auburn Football - Get all the Auburn football radio you could need, with TuneIn. You can listen to our Auburn football radio station anywhere in the country. Get all your news about Auburn football and listen live when a game is on. Just check .
UHF Gen 2 RFID tags have four memory banks: EPC; TID; User; Reserved; The .
The second-generation system (Gen-2) is favored after December 2004 and is the standard to follow when satisfying the requirements of the DoD and Wal-Mart RFID mandates. RFID tags are classified as Class 0 through Class 5, depending on their functionality: Class 0 – UHF; read . UHF Gen 2 RFID tags have four memory banks: EPC; TID; User; Reserved; The chipset, or integrated circuit (IC), houses these four memory banks and is where all the data is stored. Some chipsets have different bit allocations between the four banks to allow for more user memory or a longer EPC number. Here is a breakdown of the classes as originally proposed. • Class 1: a simple, passive, read-only backscatter tag with one-time, field-programmable non-volatile memory. • Class 2: a passive backscatter tag with up to 65 kilobytes of read-write memory. • Class 3: a semi-passive backscatter tag with up to 65 kilobytes of read memory .
Navigating the world of "Magic" RFID Cards can be difficult. Different suppliers have different badges with different abilities, and each version may have multiple generations. At Lab401, we work closely with our suppliers to ensure we have the latest and most stable versions of "Magic UID Tags". EPCglobal Inc., the organization that is developing standards for data synchronization and communication of RFID data, has ratified the UHF generation 2 (Gen2) standard for RFID tag manufacture. But what does it mean to you?The Gen 2 standard was designed to significantly improve the rate at which readers can read data from and write data to RFID tags. While Gen 1 supported a maximum data transfer rate of up to 140kbps, Gen 2 offers a data transfer rate of up to 640 kbps. In addition, tags must be written at a rate of 16 bits in under 20 milliseconds.EPC Gen 2 is short-hand for the Electronic Product Code Class-1 Generation-2 UHF RFID Protocol, the specification developed by EPCglobal for the second generation RFID air interface protocol and one example of a passive RFID tag protocol.
Abstract— In this paper, we analyze the effect of Gen2 protocol parameters on RFID tag performance (tag sensitivity and backscatter efficiency). We describe our measurement methodology and perform characterization of several tags with different latest Gen2 ICs available on the market (Monza, UCODE, and Higgs families).We are focused here on how a Gen 2 tag responds to a query command issued by a reader. Gen 2 compliant tags have two built-in modulation operations; they are known as FM0 baseband and Miller subcarrier. This post is designed to explain the difference between Search Modes and Sessions on RFID Readers, and give examples of when you should use which settings.
In early 2024, a new version of the GS1 Electronic Product Code (EPC) global Gen2 specifications — Gen2v3 — is expected, defining methods that would make RAIN RFID deployments faster and more accurate. The change is in response to the ongoing evolution of radio frequency identification. UHF Gen 2 RFID tags have four memory banks: EPC; TID; User; Reserved; The chipset, or integrated circuit (IC), houses these four memory banks and is where all the data is stored. Some chipsets have different bit allocations between the four banks to allow for more user memory or a longer EPC number. Here is a breakdown of the classes as originally proposed. • Class 1: a simple, passive, read-only backscatter tag with one-time, field-programmable non-volatile memory. • Class 2: a passive backscatter tag with up to 65 kilobytes of read-write memory. • Class 3: a semi-passive backscatter tag with up to 65 kilobytes of read memory . Navigating the world of "Magic" RFID Cards can be difficult. Different suppliers have different badges with different abilities, and each version may have multiple generations. At Lab401, we work closely with our suppliers to ensure we have the latest and most stable versions of "Magic UID Tags".
EPCglobal Inc., the organization that is developing standards for data synchronization and communication of RFID data, has ratified the UHF generation 2 (Gen2) standard for RFID tag manufacture. But what does it mean to you?
The Gen 2 standard was designed to significantly improve the rate at which readers can read data from and write data to RFID tags. While Gen 1 supported a maximum data transfer rate of up to 140kbps, Gen 2 offers a data transfer rate of up to 640 kbps. In addition, tags must be written at a rate of 16 bits in under 20 milliseconds.EPC Gen 2 is short-hand for the Electronic Product Code Class-1 Generation-2 UHF RFID Protocol, the specification developed by EPCglobal for the second generation RFID air interface protocol and one example of a passive RFID tag protocol.Abstract— In this paper, we analyze the effect of Gen2 protocol parameters on RFID tag performance (tag sensitivity and backscatter efficiency). We describe our measurement methodology and perform characterization of several tags with different latest Gen2 ICs available on the market (Monza, UCODE, and Higgs families).
rfid tags for access control
We are focused here on how a Gen 2 tag responds to a query command issued by a reader. Gen 2 compliant tags have two built-in modulation operations; they are known as FM0 baseband and Miller subcarrier. This post is designed to explain the difference between Search Modes and Sessions on RFID Readers, and give examples of when you should use which settings.
rfid tags and readers
greater anglia smart card expiry
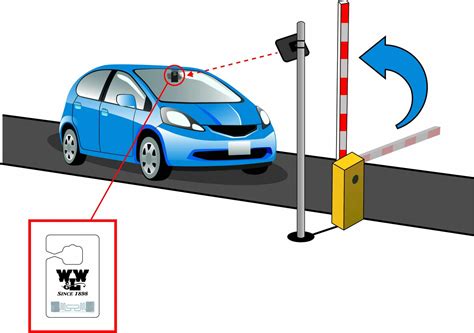
gwr smart card
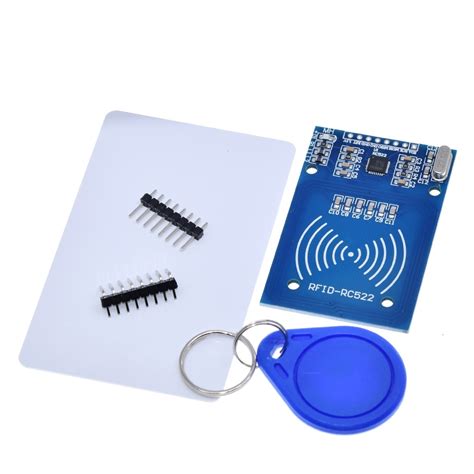

new rfid tags not working
Listen to Stream Auburn Tigers (Football) here on TuneIn! Listen anytime, anywhere! . Sports Radio 740. Unsportsmanlike with Evan, Canty and Michelle . The Game. Nashville's Best .
difference between gen2 and gen 3 rfid tags|low frequency rfid tags